
Image from: https://www.healthshots.com/healthy-eating/nutrition/balanced-diet-benefits/
Maintaining a balanced diet is fundamental to achieving optimal health and well-being. A balanced diet provides the body with essential nutrients, supports vital functions, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. This guide delves into the components of a balanced diet, practical tips for healthy eating, and the benefits of maintaining nutritional balance.
Understanding a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is comprised of a variety of foods in appropriate proportions to supply the necessary nutrients and energy for daily activities. According to the Better Health Channel, it involves consuming foods from all five major food groups:
1. Fruits and Vegetables
Rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, these should form a significant part of daily intake.
2. Grains
Opt for whole grains like brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread, which provide sustained energy and fiber.
3. Proteins
Include lean meats, poultry, fish, legumes, nuts, and seeds to support muscle health and repair.
4. Dairy and Alternatives
Sources like milk, yogurt, and cheese supply calcium and other essential nutrients.
5. Fats
Focus on healthy fats from sources such as avocados, olive oil, and nuts while limiting saturated and trans fats.
Incorporating a variety of foods from these groups ensures a comprehensive nutrient intake (Better Health Channel, 2024).
The Healthy Eating Plate Model
Developed by nutrition experts at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, the Healthy Eating Plate offers a visual guide for creating balanced meals:
- Half the Plate: Fill with fruits and vegetables, aiming for color and variety.
- A Quarter of the Plate: Allocate to whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, or whole-wheat pasta.
- A Quarter of the Plate: Dedicate to protein sources such as fish, poultry, beans, or nuts.
- Healthy Oils: Use in moderation, choosing healthy options like olive or canola oil.
- Beverages: Opt for water, limit sugary drinks, and moderate dairy consumption.
This model emphasises balance and variety, guiding individuals toward healthier eating patterns (Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 2024).
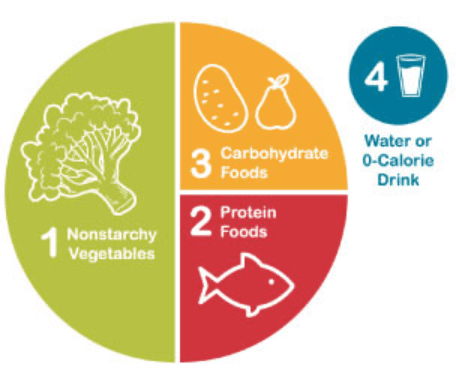
Image from: https://dconnect.co.nz/what-is-healthy-plate-model/
Practical Tips for Healthy Eating
Adopting a balanced diet involves mindful choices and habits:
- Plan Meals: Organise meals and snacks to include diverse food groups, ensuring nutrient adequacy.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of serving sizes to avoid overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of foods high in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats.
- Stay Hydrated: Aim for adequate water intake to support digestion and overall health.
- Read Labels: Understanding nutritional information helps in making informed food choices.
Implementing these strategies can lead to sustainable healthy eating habits (Healthline, 2024).
Benefits of a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet offers numerous health advantages:
- Weight Management: Supports healthy body weight and reduces obesity risk.
- Disease Prevention: Lowers the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
- Improved Mental Health: Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins are linked to better mood and cognitive function.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: Provides sustained energy throughout the day, improving productivity and physical performance.
A balanced diet is integral to overall health and longevity (Heart & Stroke Foundation, 2024).
Addressing Common Challenges
While striving for a balanced diet, individuals may encounter obstacles:
- Time Constraints: Busy schedules can lead to reliance on convenience foods. Planning and preparing meals in advance can mitigate this issue.
- Budget Limitations: Healthy eating can be cost-effective by choosing seasonal produce and bulk purchasing staples.
- Dietary Restrictions: Personal preferences or medical conditions may require alternative nutrient sources. Consulting with a nutritionist can provide tailored guidance.
Overcoming these challenges is possible with practical strategies and support (NHS, 2024).
Conclusion
Embracing a balanced diet is a cornerstone of health and well-being. By incorporating a variety of foods from all major food groups, following models like the Healthy Eating Plate, and implementing practical eating strategies, individuals can achieve nutritional balance. The benefits of such dietary patterns are profound, contributing to disease prevention, mental health, and overall vitality.

References
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. (2024). Healthy Eating Plate. Retrieved from https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/healthy-eating-plate/
- Healthline. (2024). How to Eat Healthy: A Guide to a Balanced Diet. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/how-to-eat-healthy-guide
- NHS (National Health Service). (2024). Eating a Balanced Diet: How to Eat Well. Retrieved from https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/how-to-eat-a-balanced-diet/eating-a-balanced-diet/
- Heart & Stroke Foundation. (2024). Healthy Eating Basics. Retrieved from https://www.heartandstroke.ca/healthy-living/healthy-eating/healthy-eating-basics
- Better Health Channel (Victoria, Australia). (2024). Healthy Eating and Nutrition. Retrieved from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/healthy-eating
- Healthdirect Australia. (2024). Balanced Diet and Nutrition Information. Retrieved from https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/balanced-diet


